INTRODUCTION:
In computer central processing units, micro-operations (also known as a micro-ops or μops) are detailed low-level instructions used in some designs to implement complex machine instructions (sometimes termed macro-instructions in this context).
Usually, micro-operations perform basic operations on data stored in one or more registers, including transferring data between registers or between registers and external buses of the central processing unit (CPU), and performing arithmetic or logical operations on registers. In a typical fetch-decode-execute cycle, each step of a macro-instruction is decomposed during its execution so the CPU determines and steps through a series of micro-operations. The execution of micro-operations is performed under control of the CPU’s control unit, which decides on their execution while performing various optimizations such as reordering, fusion and caching
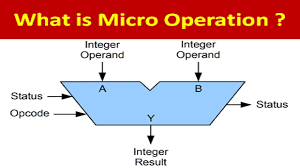
TYPES OF MICRO OPERATIONS:
The micro-operations in computers are classified into the following categories:
– Register transfer micro-operations: These type of micro operations are used to transfer from one register to another binary information.
– Arithmetic micro-operations : These micro-operations are used to perform on numeric data stored in the registers some arithmetic operations.
– Logic micro-operations: These micro operations are used to perform bit style operations / manipulations on non numeric data.
– Shift micro operations: As their name suggests they are used to perform shift operations in data store in registers.

ARITHMETIC MICRO-OPERATIONS:
We know basic arithmetic operations are Addition, Subtraction, Increment, Decrement, and Shift.
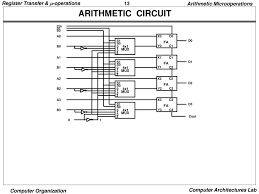
Addition Micro-operation:
(In this operation, data presented in R1 register is added with data in R2 register and result will be stored in R3 register)
Subtraction Micro-operation:
(Data presented in R2 register is subtracted from data in R1 register and result will be stored in R3 register)
One’s Complement Micro-operations:
(Data value in R2 register is first complemented then will be replaced with itself)
Like these arithmetic micro-operations there are many more micro-operations for arithmetic. But concept is same perform arithmetic operation on data values in registers and store them into the same register or another.

LOGIC MICRO-OPERATIONS:
In Logic Micro-operation there could be different operations like OR, AND, NOT, XOR etc. but these are basic micro-operation in logic type.

OR Micro-operation: –
Symbol used for OR Micro-operation is “v” or “+”. “v” this symbol is used when we are showing OR micro-operation on bits and “+” this symbol is used for showing OR micro-operation when we are using Registers (R1 , R2 etc) for implementing OR Micro-operation.
Example: – 100110 v 1010110 = 1110110
Explanation of example, in this example each bit starting from right side will be compared with OR operation and we will get result after all comparisons and in last if bits are left we can place them as it is.
AND Micro-operation: –
This is very similar to OR micro-operation but, it have different symbol and different operation that is AND Gate concept.
Symbol is “^”
Example: – 100110 ^ 1010110 = 0000110
Bits are compared from right side with AND gate operation.
In NOT Micro-operation “bar” symbol is used
Example: –
There are much more logic micro-operations are there but process of implementation is same just have their own different calculations.
Logic Micro-operations Hardware Implementation
The hardware implementation of logic micro-operations requires that logic gates be inserted for each bit or pair of bits in the registers to perform the required logic function
Most computers use only four (AND, OR, XOR, and NOT) from which all others can be derived.
Note: this is not complete package about micro-operations so if anyone has query can ask in comments below.
SHIFT MICRO-OPERATIONS:
Shift Micro Operations in computer architecture are those which are used in serial shifting of data present in a register. We can also say that Shift micro Operations move or shift data in a register bitwise that is, one bit at a time either left or right from its original position.

